|
Hashtags for the different areas and perspectives can be found here
|
|
Areas in Psychology
An area in Psychology is a paradigm: a specific way of thinking about behaviour. Most psychologists will work mainly in one area and will agree with the assumptions and principles of this paradigm. These assumptions and principles explain what the cause of behaviour is and how behaviour should be researched. |
.Perspectives in Psychology
A perspective in Psychology is a set of ideas which psychologists use to answer specific issues. For example, Social psychologists will sometimes take a Behaviourist perspective on a topic like phobias. |
5 Areas
and 2 Perspectives
|
There are 2 perspectives or ways of thinking that any psychologist may use when looking at specific behaviours. These perspectives also have distinct:
|

For each of the 5 areas and 2 perspectives, you need to be able to:
- Explain its defining principles and concepts
- Discuss research which illustrate it
- Evaluate its strengths and weaknesses
- Hypothesise applications of it
- Compare how each is different from and similar to the other areas / perspective.

Exam Paper Questions on the Areas / Perspectives
This is part of paper 2 section B.
You could be asked to
This is part of paper 2 section B.
You could be asked to
- outline the area / perspective
- explain 1 or more of its principles
- explain why a Core Study links with the area / perspective
- compare how one area / perspective is similar / different to another
- link the area / perspective to a debate

Independent Learning
Prepare your answers to these example exam questions. The students who did this in 2018 achieved the highest grades.
Prepare your answers to these example exam questions. The students who did this in 2018 achieved the highest grades.
| paper_2_section_b_question_bank.docx | |
| File Size: | 21 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
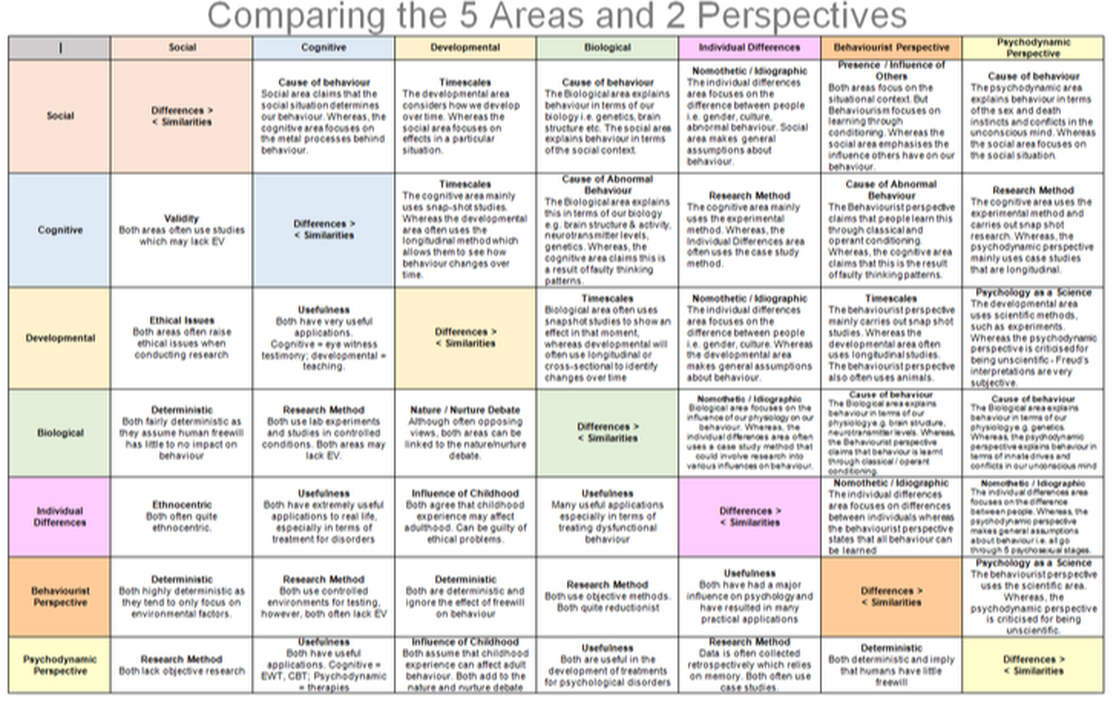
Comparing the Areas and Perspectives
This is a very difficult task to do. You need to be able to say how each are similar and different to each other. This is a popular question in Paper 2 section B.
This is a very difficult task to do. You need to be able to say how each are similar and different to each other. This is a popular question in Paper 2 section B.
|
Comparison Questions
Many students only get half marks when comparing, as they forget to do the first two things in this mark scheme.
|
| |||||||
Strengths and Weaknesses Questions
You could be asked to evaluate the areas / perspectives in Paper 2 Section B. This will mean that you have to know strengths and weaknesses of the areas in general (not just the Core Studies). Use the P-E-E-C-C structure to develop your answer.

Point
Explanation – because / this means …
Example – this is shown by the study by …
Conclusion - this matters / is helpful / is a problem because …
Challenge - however / alternatively ...
Explanation – because / this means …
Example – this is shown by the study by …
Conclusion - this matters / is helpful / is a problem because …
Challenge - however / alternatively ...

Independent Learning
Prepare your answers to the example exam questions above. The students who did this in 2018 achieved the highest grades.
Prepare your answers to the example exam questions above. The students who did this in 2018 achieved the highest grades.

Linking and Locating Questions

The specification expects you to know how each of the 20 core studies relate to their key theme and to the area of psychology it is placed within.
Remember there are 3 parts to show here:
Remember there are 3 parts to show here:
- knowledge of the key theme / areas - be prepared to explain what it means, such as referring to its principles
- knowledge of the core study - remember that good AO1 makes full use of key terms
- How #2 shows / links to #1
| linking_the_core_studies_to_the_areas.docx | |
| File Size: | 24 kb |
| File Type: | docx |

Independent Learning
Prepare your answers to this question, filling in the names of the areas / perspectives:
Explain how any 1 core study can be considered to be located within the ... area / perspective. (5)
Prepare your answers to this question, filling in the names of the areas / perspectives:
Explain how any 1 core study can be considered to be located within the ... area / perspective. (5)