Courage
Having the strength to be able to face challenges which might seem to be beyond you, and the willingness to tackle them.
Having the strength to be able to face challenges which might seem to be beyond you, and the willingness to tackle them.
Brain Dissection
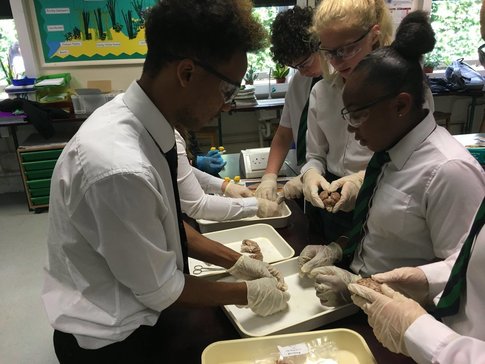
Dissecting a brain takes significant courage, especially when the brain is
- from a sheep
- has been preserved in Phenoxetol
- and still has its dura mater attached
Reading the EEG
|
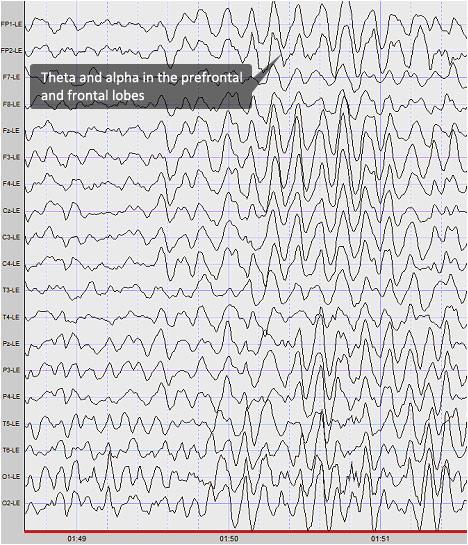
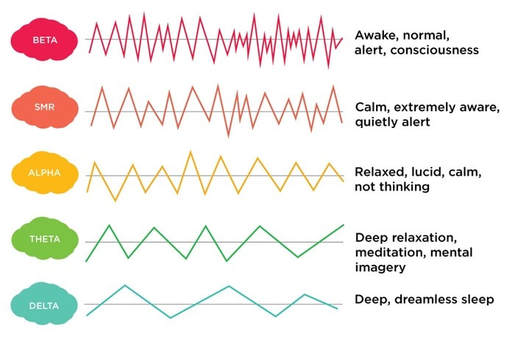
EEG is an acronym for electroencephalogram. It is a graphical representation of electrical activity from the brain.
The EEG reads scalp electrical activity generated by the cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the brain. These minute amounts of electricity are recorded by placing small electrodes on the scalp using a mesh of recording electrodes. Reading the EEG graphical display takes significant amounts of courage and training and requires our students to learn about:
|
Developing Psychological Literacy
According to McGovern, psychological literacy is being insightful and reflective about one’s own and others’ behaviour and mental processes’ and having the ability to apply ‘psychological principles to personal, social, and organisational issues in work, relationships and the broader community’.
Psychological literacy is developed through the use of self-report measures in class, allowing students to gain insight on their own behaviour and processes. Rather than being responsive to the 'psychological vanity' shown by some students ('Analyse me, Miss'), this allows students to be curious about their own Psychology. Additionally, it does require significant self-management to understand the judgements these self-reports offer.
Some of these self-report measures can be found on the Curiosity page.
According to McGovern, psychological literacy is being insightful and reflective about one’s own and others’ behaviour and mental processes’ and having the ability to apply ‘psychological principles to personal, social, and organisational issues in work, relationships and the broader community’.
Psychological literacy is developed through the use of self-report measures in class, allowing students to gain insight on their own behaviour and processes. Rather than being responsive to the 'psychological vanity' shown by some students ('Analyse me, Miss'), this allows students to be curious about their own Psychology. Additionally, it does require significant self-management to understand the judgements these self-reports offer.
Some of these self-report measures can be found on the Curiosity page.