Summary of some Methodological Issues
|

Methodological Issues appears in Paper 3
There are a greater number of methodological issues and debates to be applied in paper 3.
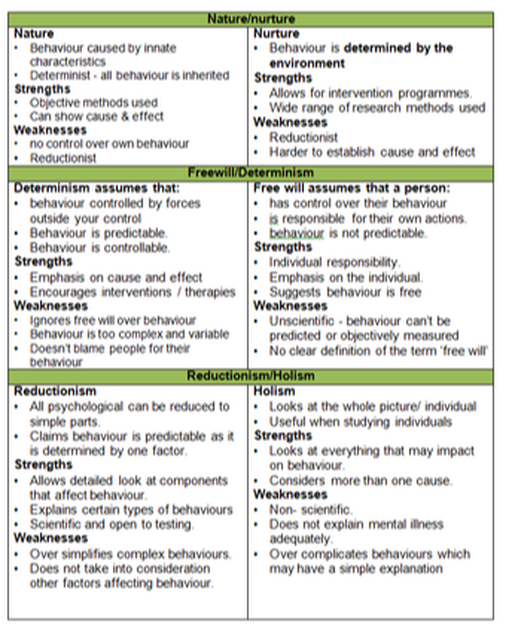
Nature/nurture
Freewill/determinism
Reductionism/holism
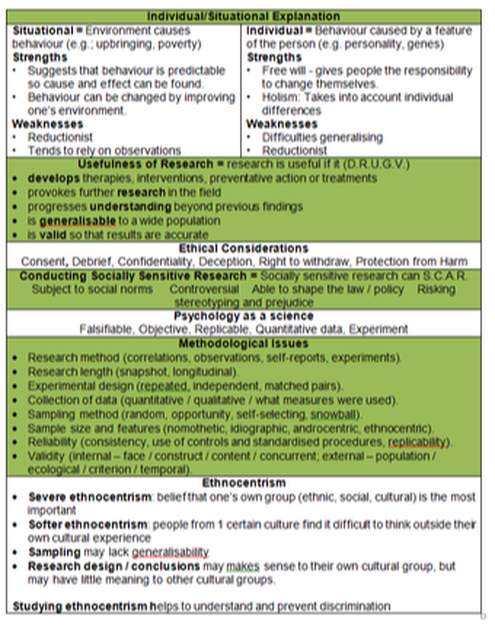
Individual/situational explanations
Usefulness of research
Ethical considerations
Conducting socially
sensitive research
Psychology as a science
Ethnocentrism
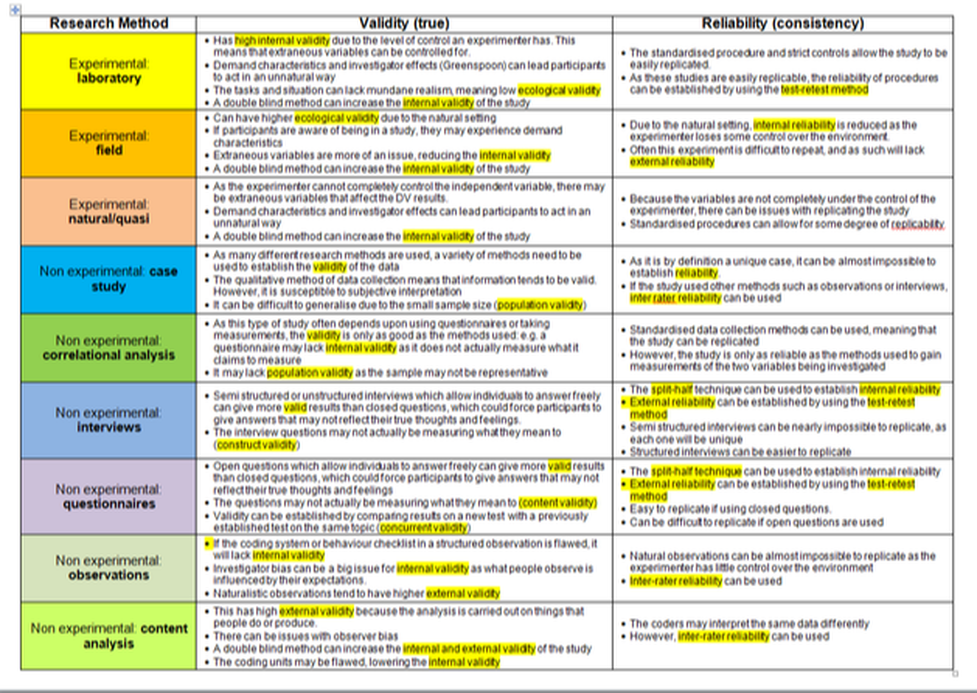
Validity
Reliability
Sampling bias
There are a greater number of methodological issues and debates to be applied in paper 3.
Nature/nurture
Freewill/determinism
Reductionism/holism
Individual/situational explanations
Usefulness of research
Ethical considerations
Conducting socially
sensitive research
Psychology as a science
Ethnocentrism
Validity
Reliability
Sampling bias
Methodological Issues of the topic area in GENERAL
These are issues with HOW the research is done on the topic area in general NOT just the Key Study.
These are issues with HOW the research is done on the topic area in general NOT just the Key Study.
|
General Research Methods for Paper 3 Options: Child
|
General Research Methods for Paper 3 Options: Crime
|
| child_and_crime_revision_methodological_issues.docx | |
| File Size: | 372 kb |
| File Type: | docx |